Let us derive the L-value of the first bit ($m=1$) of a 4-PAM modulated signal. The constellation and the mapping of input bits $x_1$ and $x_2$ are according to the following figure.
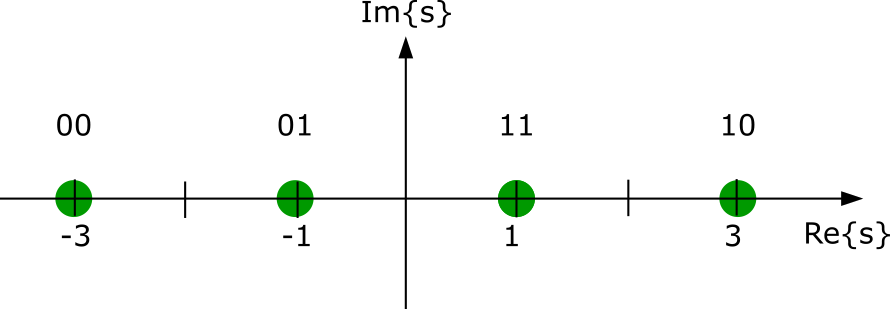
The first bit is 1 for $s=+1$ and $s=-1$, and 0 for $s=+3$ and $s=-3$. Thus, the L-value of bit 1 is calculated as \[ L(x_{1}|y) = \ln \frac{p(y|s=+1) \cdot P[x_1=1] \cdot P[x_2 = 1] +p(y|s=-1)\cdot P[x_1=1] \cdot P[x_2 = 0] }{p(y|s=+3)\cdot P[x_1=0] \cdot P[x_2 = 1] +p(y|s=-3)\cdot P[x_1=0] \cdot P[x_2 = 0] }. \] For the given AWGN-channel it holds \[ L(x_{1}|y) = L_A(x_1) + \ln \frac{ \exp(\frac{-(y-1)^2}{2\sigma^2}) + \exp(\frac{-(y+1)^2}{2\sigma^2}) \cdot \exp \left[ L_A(x_2) \right] }{ \exp(\frac{-(y-3)^2}{2\sigma^2}) + \exp(\frac{-(y+3)^2}{2\sigma^2}) \cdot \exp \left[ L_A(x_2) \right] }. \]
