Block LDPC
Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes can be defined by a parity check matrix $\boldsymbol{H}$, it holds for each code word $\boldsymbol{v}$ that
$$\boldsymbol{H\cdot v^{\mathsf{T}}}=\boldsymbol{0}$$
A regular block $\left(\mathit{d_{v},d_{c}}\right)$ LDPC code has variable node degree $d_{v}$ and check node degree $d_{c}$, which equals the column (row)-weight of $\boldsymbol{H}$.
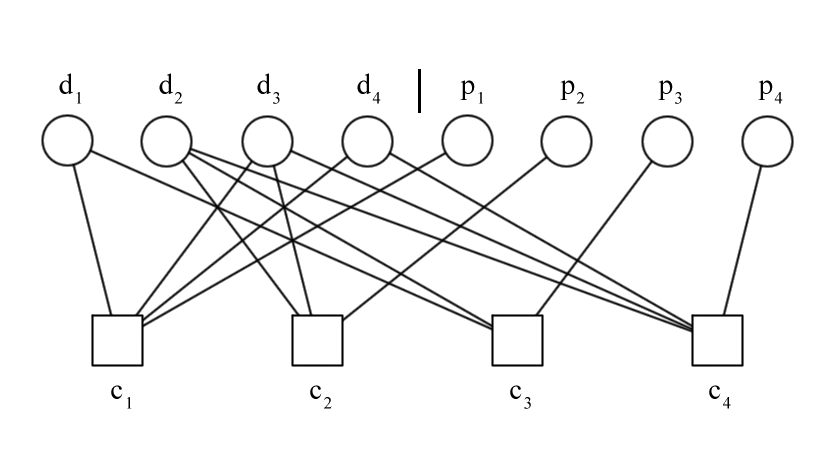
Example and Tanner Graph
${k=4}$ information bits and ${m=4}$ parity bits
$$\mathbf{H=(P\mid I)=\left[\mathrm{\begin{array}{cccccccc}
1 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\
0 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\
1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\
0 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}}\right]}$$
$\mathbf{H}$ can be represented by a bipartite graph, so-called Tanner graph [1]